The Progress of the PURGES Process
2 December, 2024
The PURGES process is an innovative approach to transforming industrial waste into valuable resources. Originally developed to provide a new use for waste from Cobre Las Cruces—a mining and hydrometallurgical complex in southern Spain known for producing high-purity copper—this process focuses on recovering cobalt, a crucial element for modern technologies like batteries.
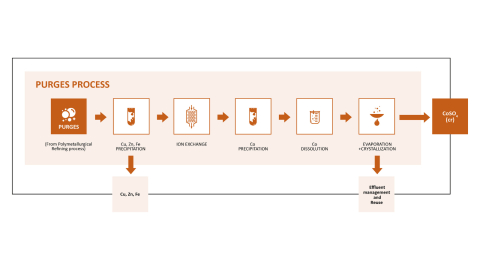
Cobalt is a highly valuable component found in small quantities in the mineral ore and is currently neither processed nor recovered at the facility. The PURGES process aims to offer a way to recover up to 500 tons of cobalt per year from liquid waste streams. The goal of the Purges process is to recover at least 90% of the cobalt with over 99% purity, creating cobalt sulphate (CoSO₄), a critical material for lithium-ion battery cathodes.
The process is challenging, since the liquid waste stream contains not just cobalt but also high amounts of calcium, manganese, and traces of other metals like iron, zinc, and copper. The task lies in isolating cobalt from the other elements meeting the high purity requirements for battery production.
The process starts with a stage of polishing and filtration in which traces of unwanted metals like copper, zinc, and iron are removed, and the liquid is treated to convert remaining sulphides into sulphates. Then the solution is passed through an ion-exchange column filled with a specialized resin that strongly binds cobalt. This step separates cobalt from calcium and manganese, which remain in the solution. The trapped cobalt is released from the resin using acid, creating a solution with about 20 times the initial cobalt concentration. Advanced membrane technology minimizes waste by recovering and recycling excess acid. Finally, the purified cobalt is precipitated into a solid form, then converted into cobalt sulphate through controlled reactions and crystallization.
The result is a high-purity cobalt product ready to support the growing demand for sustainable energy storage. Future improvements of this route could include recovering manganese from the process, further enhancing resource efficiency. By unlocking the potential of industrial waste, the PURGES process not only reduces environmental impact but also contributes to the development of greener technologies.

.jpg)